Introduction
Bariatric surgery refers to a variety of surgical procedures performed to help people with obesity lose weight. These surgeries alter the gastrointestinal system by limiting food intake and/or reducing nutrient absorption. Over the past few decades, bariatric surgery has become an increasingly popular weight loss option for those with severe obesity. Studies show bariatric surgery can lead to significant long-term weight loss and improvements in obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, sleep apnea, and arthritis.
However, bariatric surgery is not for everyone. It is essential to choose the right type of surgery based on individual factors like body mass index (BMI), overall health, lifestyle, goals, and risk tolerance. Consulting with a knowledgeable bariatric surgeon and healthcare team is key to determining if surgery is appropriate, which procedure is optimal, and how to prepare for surgery and the extensive lifestyle changes required for success. This article explores the various types of bariatric surgery, considerations in choosing between them, and the importance of guidance from a multidisciplinary healthcare team.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
There are several types of bariatric surgery, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The four main procedures are:
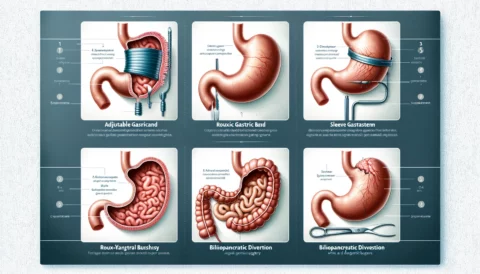
Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap Band)
Description: This procedure involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper portion of the stomach. Tightening or loosening the band via a port placed under the skin controls the size of the stomach pouch above the band. This creates a sense of fullness with smaller meals.
Advantages: Lap band surgery is reversible and adjustable. It causes minimal vitamin/mineral deficiencies and has a lower complication rate than other surgeries.
Disadvantages: The band requires periodic adjustments to tighten or loosen it. Weight loss may be slower and less dramatic compared to other bariatric surgeries. Some patients don’t lose much weight. Band slippage and erosion can occur.
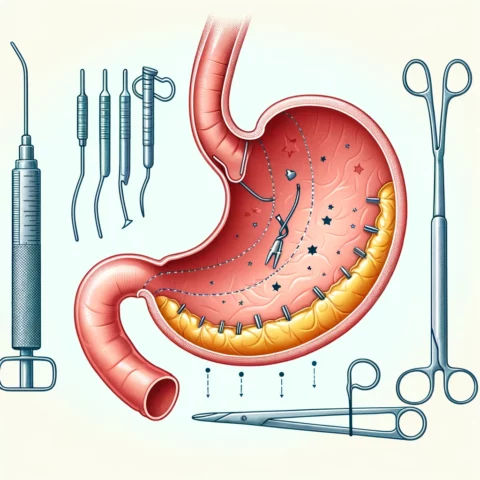
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Description: This procedure removes approximately 80% of the stomach, creating a tubular pouch that resembles a banana. This restricts food intake and reduces appetite by decreasing production of the hunger hormone ghrelin.
Advantages: Sleeve gastrectomy typically leads to greater weight loss than gastric banding, resulting in 60-70% excess weight loss. It requires no foreign objects or intestinal rerouting.
Disadvantages: The procedure is irreversible. Potential complications include leaks in the sleeve and nutritional deficiencies. Some may experience dumping syndrome.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Description: This surgery creates a small stomach pouch and attaches it directly to the middle portion of the small intestine. Food bypasses the rest of the stomach and upper small intestine. This limits food intake and absorption of calories.
Advantages: Gastric bypass typically leads to greater weight loss than banding or sleeve gastrectomy, resulting in 70-80% excess weight loss. It also improves obesity-related conditions like diabetes.
Disadvantages: It involves intestinal rerouting and more risk of complications. Dumping syndrome is common. Lifelong nutritional supplementation is required.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS)
Description: This two-part procedure involves sleeve gastrectomy and intestinal rerouting. The pyloric valve is preserved while a large portion of the small intestine is bypassed. This significantly restricts food absorption.
Advantages: BPD-DS produces the greatest weight loss of all bariatric surgeries, resulting in 70-80% excess weight loss. It also leads to improvement or remission of type 2 diabetes.
Disadvantages: The complex rerouting increases surgical risks and malnutrition. Patients require lifelong vitamins/minerals through injections or monthly monitoring.
Choosing the Right Bariatric Surgery
Selecting the most appropriate bariatric procedure for an individual requires considering several factors and having in-depth discussions with a bariatric surgery team.
Factors to Consider
- Body mass index (BMI): Procedures like gastric bypass and duodenal switch are usually reserved for those with a BMI of 40 or higher. Sleeve gastrectomy may be recommended for BMIs between 35 and 40. Banding can be considered for BMIs as low as 30.
- Health conditions: Those with obesity-related conditions like diabetes or heart disease may benefit more from procedures like gastric bypass that typically produce greater weight loss.
- Lifestyle: Procedures requiring frequent monitoring and strict dietary compliance may not be optimal for those unable or unwilling to commit.
- Goals: Those seeking maximum weight loss may prefer gastric bypass or BPD-DS, while others may opt for lower-risk procedures.
- Risk tolerance: Procedures with higher complication rates like gastric bypass or BPD-DS require consideration of surgical risks versus benefits.
Consulting with a Healthcare Team
- Bariatric surgeon evaluation: A thorough assessment includes review of medical history, BMI, diagnostics tests, and discussion of procedure options and associated risks.
- Discussion of needs and concerns: Ongoing, open conversations with the surgeon allow clarification of expectations, addressing fears and anxieties, and voicing preferences.
- Guidance on optimal procedure: The surgeon will provide feedback on which procedures may be most appropriate given the evaluation results and individual factors.
- Preparation for surgery: The team provides instruction on dietary changes, smoking cessation, and other preparations needed weeks before surgery.
- Post-operative care: Follow-up care includes dietary modifications, guidelines for physical activity, and supplementation if needed. Lifestyle counseling helps adjust to changes.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery can be a life-changing weight loss tool for those suffering from severe obesity and related health conditions. However, the choice of surgery should not be taken lightly given the risks involved and the significant lifestyle modifications required for success. Thorough research and open discussions with a knowledgeable bariatric surgery team are key to determining if surgery is the right choice. The team can then guide each individual in selecting the safest and most effective procedure based on unique circumstances and goals. With proper selection and preparation, bariatric surgery can help morbidly obese patients improve their health, quality of life, and longevity.